7.3. Hough Circle Transform¶
In this chapter,
We will learn to use Hough Transform to find circles in an image.
We will see these functions: cv2.HoughCircles()
7.3.1. Theory¶
A circle is represented mathematically as \((x-x_{center})^2 + (y - y_{center})^2 = r^2\) where \((x_{center},y_{center})\) is the center of the circle, and \(r\) is the radius of the circle. From equation, we can see we have 3 parameters, so we need a 3D accumulator for hough transform, which would be highly ineffective. So OpenCV uses more trickier method, Hough Gradient Method which uses the gradient information of edges.
The function we use here is cv2.HoughCircles(). It has plenty of arguments which are well explained in the documentation. So we directly go to the code.
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> import numpy as np
>>> import cv2 as cv
>>> img = cv.imread('/cvdata/opencv-logo-white.png',0)
>>> img = cv.medianBlur(img,5)
>>> cimg = cv.cvtColor(img,cv.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
>>> circles = cv.HoughCircles(img,cv.HOUGH_GRADIENT,1,20,
>>> param1=50,param2=30,minRadius=0,maxRadius=0)
>>> circles = np.uint16(np.around(circles))
>>> for i in circles[0,:]:
>>> # draw the outer circle
>>> cv.circle(cimg,(i[0],i[1]),i[2],(0,255,0),2)
>>> # draw the center of the circle
>>> cv.circle(cimg,(i[0],i[1]),2,(0,0,255),3)
>>>
>>> # cv.imshow('detected circles',cimg)
>>> # cv.waitKey(0)
>>> # cv.destroyAllWindows()
>>> plt.imshow(cimg)
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x7efbd248ae50>
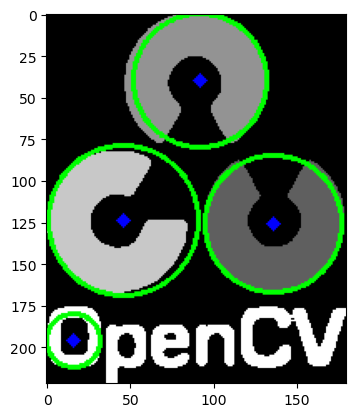
Result is shown below: